

You can also calculate the instantaneous slope of any function at any x value using limits and the average rate of change formula. The derivative is a function that can tell you the instantaneous slope of a function at any x value. Limits and theyre equal, in which case the ordinary limit exists and is the same. We introduce the concept of a limit with simple graphs and practical examples. Sometimes we have both Left-Hand and Right-Hand. Learning limits is important because it ties in nicely with the second major topic taught in calculus which is Derivatives. This course focuses on the very first topic taught in Calculus - Limit Theory. This section covers the main topics that you will typically encounter on your first major calculus exam. How do derivatives depend on limits Just how are.
LIMITS IN CALCULUS HOW TO
That's the magic of calculus in a very small nutshell. This is not just a course about how to use calculus, but a mathematics course about what calculus is. Once it's straight, you can analyze the curve with regular-old algebra and geometry. Limits sort of enable you to zoom in on the graph of a curve further and further until it becomes straight. Limits of Special Trigonometric Functions - Sine, Cosine, and Tangent - Trigonometry The mathematics of limits underlies all of calculus. Limits of Rational Functions With Square Rootsĩ. This means that learning about limits will pave the way for a stronger foundation and better understanding of calculus. Predicting and approximating the value of a certain set of quantities and even functions is an important goal of calculus. Limits of Rational Functions and FractionsĨ. Limits are the foundation of calculus differential and integral calculus. Evaluating Limits By Factoring - GCF, Difference of Perfect Squares & Sum of Cubes, & Factoring By Groupingħ. Properties of Limits - Multiplication and Divisionĥ.
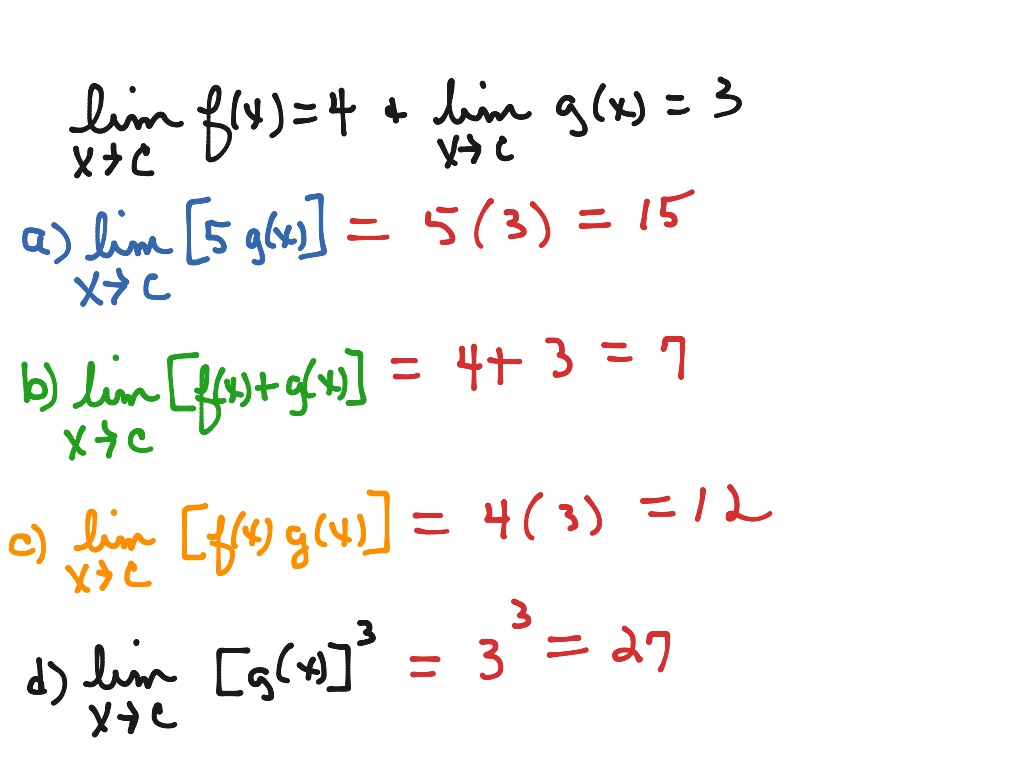
Finding The Limit of Trigonometric FunctionsĤ. If a function is defined on either side of a, but the limit as x approaches a is infinity or negative infinity, then the function has an infinite limit. the left-hand limit () is 3.8 the right-hand limit (+) is 1. Evaluating Limits Analytically Using Direct Substitutionģ. Here is a list of topics covered in this video.Ģ. In this panel, we will try to break down the cases and explain the various ways these terms can be used as well as how we use them here at 17calculus.This course is designed for high school and college students taking their first semester of calculus and who are learning limits and continuity. The use of the terms finite limits, infinite limits and limits at infinity are used differently in various books and your instructor may have their own idea of what they mean. If the values of f(x) get closer and closer, as close as we want, to one number L as we take values of x very close to (but not equal to) a.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
